Growing grapes in Colorado can be a rewarding experience, whether you’re aiming for fresh table grapes, juice, or even homemade wine. This guide will walk you through the essential steps for successful grape cultivation, from choosing the right cultivars to planting, trellising, pruning, and general care.

Types and Cultivars
Types of Grapes:
- Table Grapes: Ideal for fresh eating, with popular seedless varieties like Himrod, Interlaken, Canadice, St. Theresa, and Reliance.
- Juice and Jelly Grapes: Popular cultivars include Concord, Valiant, Niagara, and St. Croix.
- Wine Grapes
- Raisin Grapes
Cultivars:
- American Cultivars (Vitis labrusca): Known for their strong “foxy” (musty) flavor and aroma, these are used for juice, fresh eating, and some wines.
- European Cultivars (Vitis vinifera): With tight clusters and thin skins, these grapes are used for wines and require more heat units for maturity, making them less suitable for Colorado.
- French-American Hybrids: Popular for wine, with characteristics that vary depending on parentage.
Planting Grapes
Grapes need full sun and protection from wind. Space plants 6 to 8 feet apart, in rows 6 to 10 feet apart, depending on your trellising system. Strong trellising systems are necessary to support the heavy vines and fruit. Use treated posts and 12-gauge or heavier wire.

Trellising and Pruning
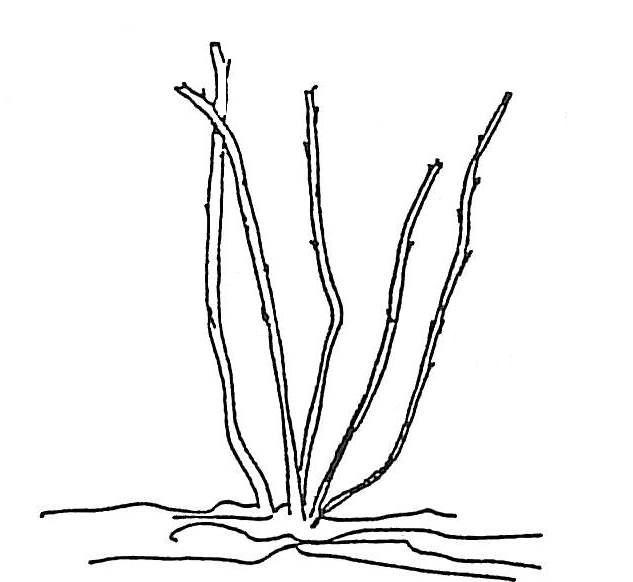
Grapes fruit on one-year-old wood, making pruning a balance between fruit production and renewing wood. Proper pruning is essential for high yields and large clusters of grapes. Unpruned or under-pruned grapes will produce many small clusters of tiny grapes, while over-pruning reduces yield.
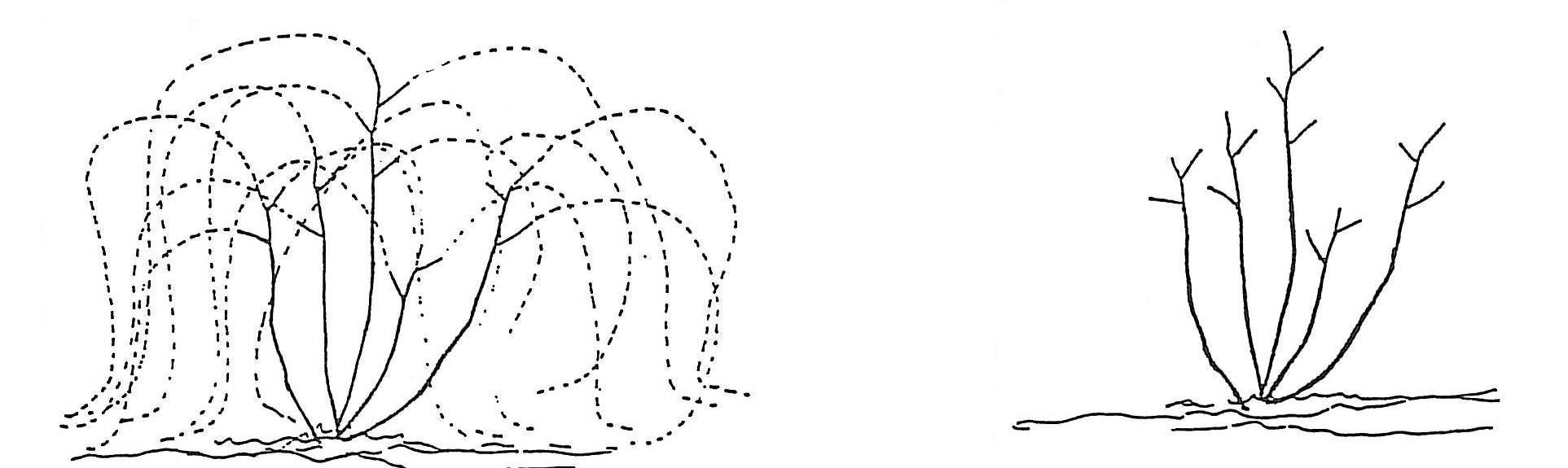
Single Curtain System:
- Pruning at Planting: Cut back to two to three buds to encourage the growth of a strong primary trunk.
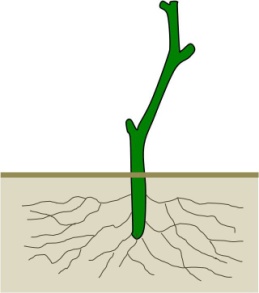 Image provided by CSU extension
Image provided by CSU extension
- Second Spring Pruning: Select one cane to become the trunk and remove others, leaving one or two renewal spurs.
 Image provided by CSU extension
Image provided by CSU extension
- Third Spring Pruning: Select two one-year-old canes to become fruiting canes and cordon arms along the trellis. Prune two other canes back to two buds each to serve as renewal spurs.
 Image provided by CSU extension
Image provided by CSU extension
- Fourth Spring and Beyond: Continue selecting new fruiting canes and renewal spurs each spring, maintaining the balance between fruit production and new wood growth.
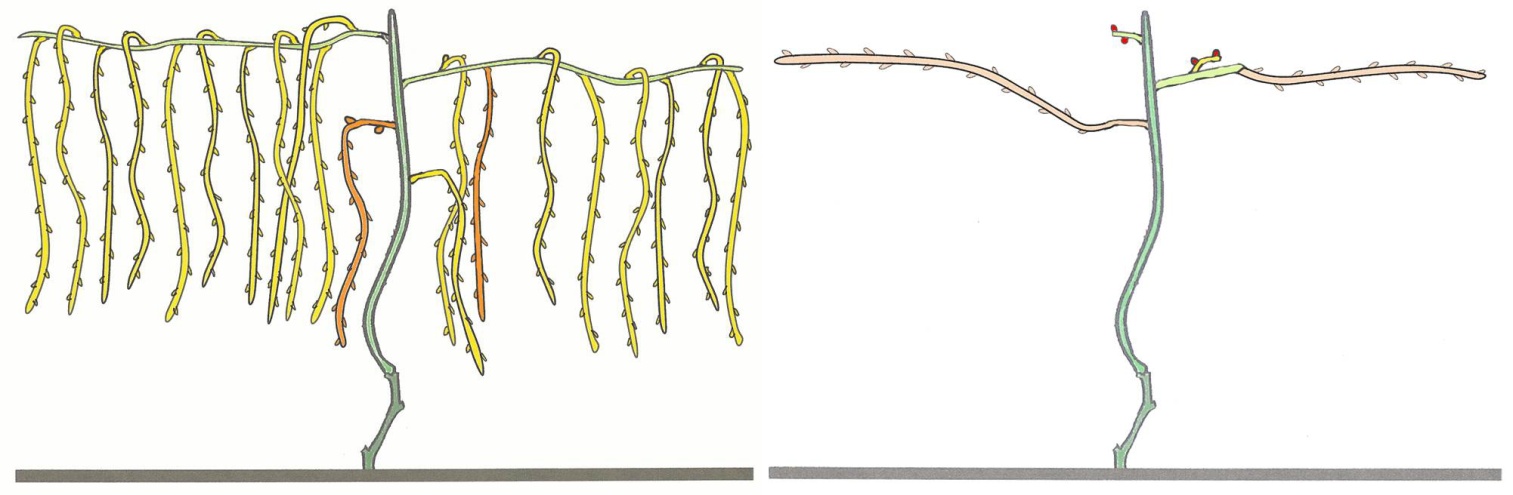 Image provided by CSU extension
Image provided by CSU extension
General Care of Grapes
- Mulching: Use a four-foot-wide weed-free bark/wood chip mulch strip under the trellis to help retain moisture and reduce weed competition.
- Watering: Avoid over-watering, as it can lead to iron chlorosis.
- Fertilization: Go light on fertilization. Apply one-fourth cup of 21-0-0 (or equivalent) per established plant, broadcast under the trellis, and water in.
- Harvest: Flavor is the best indicator for home gardeners to determine harvest time.
Common Grape Pests
Fruit:
- Birds: Bird netting may be necessary to protect the fruit.
- Botrytis Bunch Rot: Often a problem with heavy canopies due to inadequate pruning and poor air circulation.
- Spotted Wing Drosophila Flies: These can affect ripe grapes.
Plants:
- Powdery Mildew: Refer to CSU Extension Fact Sheet #2.902 for management.
- Iron Chlorosis: Typically a symptom of over-watering. Refer to CSU Extension CMG GardenNotes #223 for more information.
- Root Rots: Poor soil drainage can lead to root rot issues.
- Weeds and Diseases: Grapes do not tolerate competition well, so adequate control is necessary.
By following these guidelines, you can enjoy a bountiful grape harvest in your Colorado garden. Happy gardening!
For more detailed information, call or visit Echter’s Garden Center or contact your local CSU Extension office.